Patch Cable vs. Crossover Cable: What Is the Difference?
Stephane
Despite advances in wireless technologies, many computer networks still rely on cables as a physical medium for devices to transfer data. Several standard types of network cable exist, including coaxial cable, twisted pair cable, USB cable, crossover cable, Ethernet patch cable, fiber optic cable, etc. Among these different types of network cable, many people may be unfamiliar with the patch cable and crossover cable. In fact, patch cable and crossover cable are two types of Ethernet cable, and they have the same physical characteristics. But what on earth is the difference between the patch cable and crossover cable?
T-568A vs. T-568B
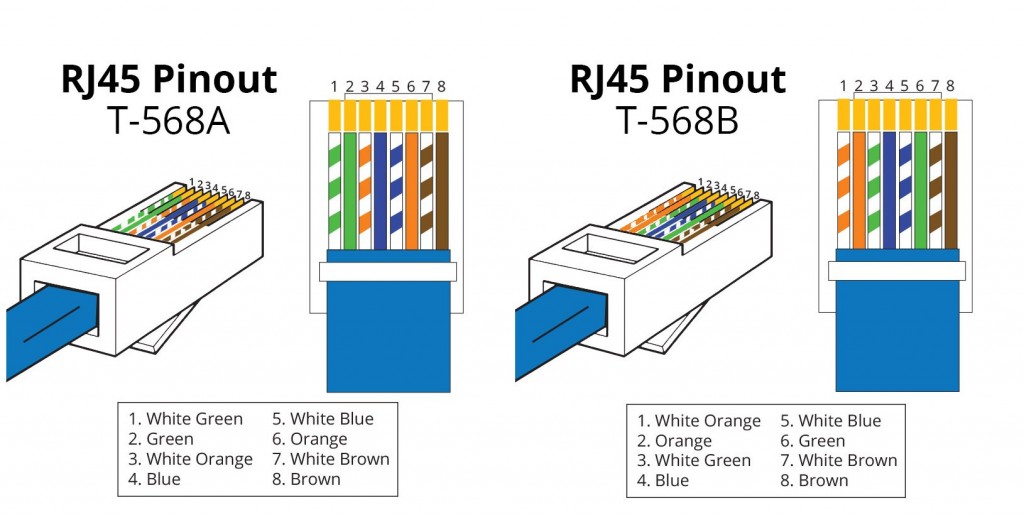
Before talking about patch cable and crossover cable, it’s very necessary to learn about the T-568A and T-568B standard. With regard to these two patch cable wiring schemes, there are two different connectivity forms. The T-568B wiring scheme is by far the most common, though many devices support the T-568A wiring scheme as well. If both ends of the patch cords are wired on the basis of one standard, it is a straight through connection. Both the standards can be used for straight through cable. If not, it is a crossover connection. Some networking applications require an Ethernet crossover cable, which has a T-568A connector on one end and a T-568B connector on the other. This type of cable is typically used for direct computer-to-computer connections. The following section will introduce the straight through cable (or patch cable) and crossover cable in details.
What Is a Patch Cable?
Many networking professionals use the term patch cable to refer to any kind of straight through cable. So a patch cable is often called a straight through cable. In other words, patch cable does not change or swap along its way. Both ends use the same wiring standard: T-568A or T-568B. So both side (connector A and connector B) of patch cable have wire arrangement with same patch cable colors (as shown in the following picture). Specifically, Pin 1 on connector A goes to Pin 1 on connector B, Pin 2 to Pin 2, etc. These patch cables are widely used for connecting the computer to the switches, hubs, or routers.

What Is Crossover Cable?
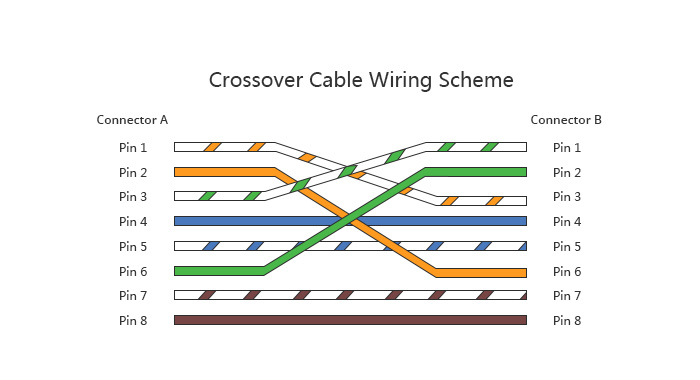
Crossover cable, as the name suggests, cross over or swap on its way when coming from one end to the other. Unlike patch cable, crossover cable uses two different wiring standards on both end: one end uses the T568A wiring standard, and the other end uses the T568B wiring standard. Both side (connector A and connector B) of crossover cable have wire arrangement with different color, and the wires that come out of the connector A should match the correct pin at the connector B. As shown in the following wiring scheme, you can see that Pin 1 on connector A goes to Pin 3 on connector B, pin 2 to pin 6, pin 3 to pin 1 and pin 6 to pin 2, etc. The crossover cables are mainly used for connecting two routers, computers, or hubs.
Patch Cables vs. Crossover Cable: When to Use?
In brief, a crossover cable connects two devices of the same type to communicate together, like a PC to a PC, or a switch to a switch. The patch cable connects two different devices to each other, like a PC and a switch. The following scenarios will explain the different applications.
Scenario 1: PC to PC
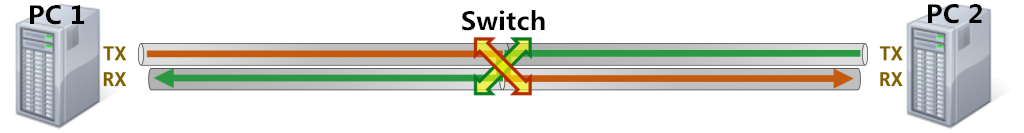
If we have two computers connected directly to each other. And both PCs try to transmit on TX wire, their signals will collide. Moreover, nothing will be sent on RX wire. Therefore, neither computer will be able to receive anything. At this point, the crossover cable is needed to make connections between two PCs. Since this kind of cable is crossed, the signal sent on TX wire from PC 1 can be received on the RX wire of PC 2. This is the reason why the crossover cables are often used to connect two same devices.
Scenario 2: PC to Switch to PC
What happens if a switch is mixed between two computers? In fact, switch is designed to communicate in between two computers, which has an innate crossing of the wires. Therefore, we do not need the cable to cross for us. What the PC 1 sends on its TX wire is received by the switch on its RX wire, and then transmits on its TX wire, finally is received by the other PC's RX wire. And vice versa. Therefore, when a switch is connected to a PC, it can simply use a patch cable.

Scenario 3: PC to Switch to Switch to PC
What then happens if we have two switches in the mix? Two switches separately cross the wire once, therefore another pair crossing in between the switches is emerges. As mentioned above, two same devices need a cross cable to make a connection. From the diagram above, we can see:
(1) When PC 1 connects to the Switch 1, we require a patch cable.
(2) When Switch 1 connects to the Switch 2, we require a crossover cable.
(3) When Switch 2 connects to the PC 2, we require a patch cable.

Conclusion
All in all, to determine if you have a patch cable or a crossover cable, what you need consider are the wiring of the cable and the situation in which you will use the cable. FS.COM offers a full range of colored patch cables (straight-through) including Cat5e patch cables, Cat6, Cat6a and Cat7 cables to meet your network requirements. In addition, network patch panels, network tools, Ethernet bulk cables and other cable assemblies are also available. For more information, please contact us over sales@fs.com.
Related Article: Quick View of Ethernet Cables Cat5, Cat5e And Cat6Running 10GBASE-T Over Cat6 vs Cat6a vs Cat7 Cabling?Home Ethernet Wiring Guide: How to Get a Wired Home Network?
Related Articles
MTP® vs MPO Cable: What Are the Differences?
Migelle March 9, 2020 There comes a more demanding request for higher transmission speed and larger capacity with the prevalence of cloud computing in the era of big data. 40/100G networks are increasingly becoming more commonplace in data centers. ...Wireless AP vs Range Extender: Which Wi-Fi Solution Is Better?
Howard September 8, 2020 If you are searching for solutions to extend the wireless network, you may encounter several hardware devices that offer the function, among which wireless access points (AP) or range extenders are on the list. There are many ...Gateway vs Firewall: What Are the Differences?
lee November 17, 2020 Network security is one of the most important aspects to consider when working over the internet, LAN or other methods, no matter how small or big your business is. Both gateways and firewalls are important network protection ...A Comprehensive Guide to MTP® Connector
Howard July 21, 2020 MTP® connector is a component widely applied in high-density network applications such as most data centers, broadcast communications, and industrial control applications, and MTP® cabling has been welcomed by a large number of ...Reference Guide: MTP/MPO Cabling for 400G Networks
Worton March 18, 2020 Introduced in late 2018 and early 2019, the 400G switch entered the market and many expected that 400G would see real adoption in 2020. In fact, the data center market analyst Dell'Oro predicts that the shipments of 400G switch ...